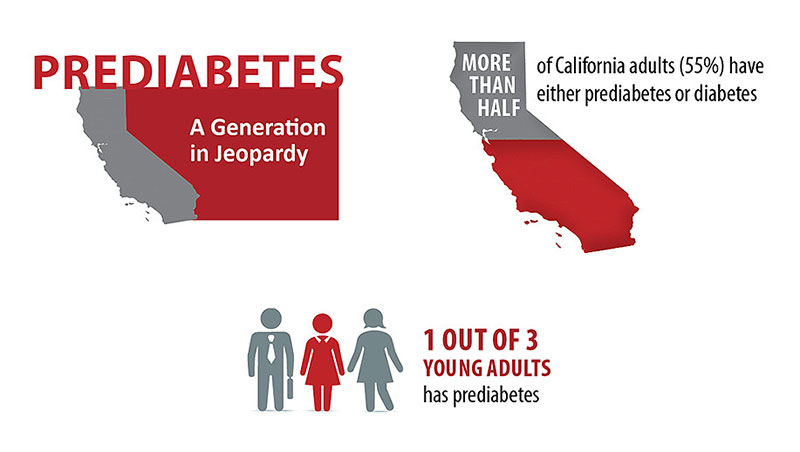
Diabetes continues to be a significant public health issue in California, affecting millions of residents across diverse communities. Understanding the latest statistics is crucial for tailoring effective prevention and treatment strategies.
The 2023 statistics underscore the urgent need for continued efforts in diabetes prevention, education, and access to healthcare in California. Targeted interventions, particularly in high-risk communities, can help curb the growing prevalence of this disease and reduce its long-term impact on public health.
Sources: California Department of Public Health (CDPH), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), American Diabetes Association (ADA)
200 W. Mines Ave Montebello CA 90640
P.O Box 1347 Montebello, CA 90640 (Mailing Address)
Office: (323) 837-9869
Email: info@lda.org
© 2024 Latino Diabetes Association